| Problem 1
Thermodynamics
Home Page |
||
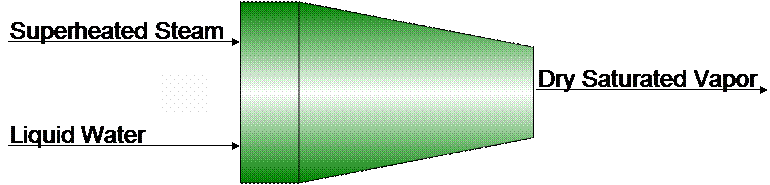 |
In
situations when only superheated steam is available a need for
saturated steam arises. The required saturated steam can be obtained be
desuperheating the superheated steam. This can be accomplished in an
adiabatic desuperheater in which liquid water is sprayed into the
superheated steam in such amounts that dry saturated steam leaves the
superheater. The following data from such a superheater is available.
Superheated steam at 320 °C, 3 MPa enters the desuperheater at a
flow rate of M kg/s. Liquid
water enters the desuperheater at 40 °C, 5
MPa. Dry saturated vapor leaves at 3 MPa. Determine the mass flow rate,
in kg/s, of liquid water required. 8 Steps to Engineering Problem Solving: 1. Abstract Problem 2. List Variables 3. State Basis of Calculations 4. Make/State Assumptions 5. List References 6. Develop Model Equations 7. Solve Equations 8. Interpret Solutions, Make Conclusions |
|